Aloe vera benefits range from natural remedies like rubbing on inflamed skin to soothe the area to manufactured products like aloe soap. Aloe has been used in the past as herbal medicine in Sub-Saharan African households to alleviate stomach upsets and clear skin blemishes.
Today, aloe vera has found widespread popularity in the beauty industry, as it is formulated in skin products like facial toners, cleansers, and lip balms to target conditions such as acne and sunburns.
Aloe Vera Description and constituents
Aloe vera is an herb belonging to the family Liliaceae. Its various species include aloe perryi, aloe linn/officinalis, aloe barbadensis, and aloe ferox. They are found in east and southern Africa, west Indies, the border of the mediterranean and tropical areas. Aloe vera does well in light sandy and medium loamy soils and is generally well tolerated in drought and dry areas. Aloe is xerophytic and propagated by seeds.
Aloe leaves grow outward in a rosette pattern. It is similar in shape to a sword, and it has spikes on the edges. It is succulent, with the insides made of water in a translucent, slippery gel and the outsides thick with a green appearance. The gel is surrounded by latex, a yellowish protective layer that demonstrates a laxative property. Aloe contains vitamin E, crystalline aloin, acemannan, barbaloin, resin, and aloe-emodin that contribute to aloe vera uses and medicinal benefits.
Aloe vera cultivation

Aloe can be farmed in greenhouses at a temperature of 16 degrees Celsius for up to 6 months. If growing it naturally, the ideal temperature is between 25-35 degrees in warm, dry areas that allow for sunlight exposure of up to 8 hours daily. Use sandy or loamy soil mixed with gravel to ensure proper drainage. If at home, mix regular gardening soil with equal parts compost and river sand.
Propagate aloe with the small offshoots that grow on the base of the main plant (the ‘pups’). Alternatively, seeds can be harvested from mature outdoor plants or brought and planted, but propagation remains the easiest way to do so. Aloe should be watered deeply and allowed to sit for a while before rewatering. Too much water rots the roots. Thus, always ensure proper drainage even in rainy seasons.
Leaves are cut near the base and kept in kerosene tins. The gel is extracted by incision, then putting pressure on the cells such that the juice from the leaves is drained out. In some instances, spontaneous evaporation or boiling until consistent, then thickening with honey, is used to prepare the gel. The gel can be packed in tight cases or further evaporated to reduce moisture content and ensure a longer shelf life.
ALOE VERA BENEFITS AND TRADITIONAL USES
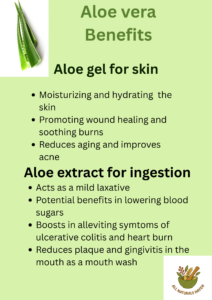
Aloe Vera Traditional Uses
In sub-Saharan Africa there are reports of aloe being used as a purgative, stimulant, and tonic due to its exertion on the small intestines to treat gastrointestinal disorders.
The aloe vera gel has also been used as a treatment for skin conditions such as rashes, burns, and wounds to promote healing. In high doses, it was also used as an abortifacient, but in low doses, it was used to stimulate blood flow to the pelvic muscle and promote menses in women with menstrual problems (an emmenagogue).
Aloe Vera Benefits and Pharmacological profile
- Used as topical medication for acne, psoriasis, cold sores, dry skin, and rashes. Formulated as skin cosmetics in soap, body gels, and lotions.
- In vitro studies with cats and dogs via topical application elicited faster wound shrinkage, reduced healing time, and better scarring compared to silver sulfadiazine. Drudi D 2018
- As a relief for constipation. Aloe contains anthraquinones that increase water content and stimulate peristalsis, thus promoting bowel emptying and relieving symptoms of constipation. Ru ying tang 2022
- As a vermifuge and repellent. Aloe has shown activity against Conchorca onchengi when ingested through polyphenol oxidative stress and improves tungiasis outcome when mixed with coconut-based oil repellent. M. Thieleke 2013
- As an antibacterial. When formulated in a mouthwash by reduction of dental plaque. It works just as well as chlorhexidine with the advantage of not staining teeth. Bushra 2014
- Use as an anti-inflammatory agent. In ulcerative colitis, it has been proven to reduce associated pain and bloating. The study used 100 ml of aloe vera gel twice daily over 4 weeks. Langmead L 2004
The gel emulsion has also been reported to alleviate symptoms of peptic ulcers in a small rat model study (Amila A kamel 2024.) The extract containing allantoin has also been reported to reduce lesions associated with aphthous stomatitis.
- As a hepatoprotective. Parental administration of aloe vera has been reported to combat ALT levels in chronic hepatitis and also protects the liver from chemical injury. YJ Fan 1989
ALOE VERA DOSING
Aloe can be used as:
A gel– cut and applied directly on the skin. Or gel extracted and heated to a concentrate.
Resin– the dried part that can be ingested and acts as a cathartic in small doses.
Powder– dried extract ground into powder and reconstituted as a supplement capsule (alongside other ingredients) or put in tea bags/muslin bags and used as infusions.
Cosmetics– soaps, lip balms, jellies, and lotions.
- 500 mg twice daily in metabolic syndrome for 8 weeks.
- Applied after every 6 hours for frostbite and generally thrice or twice daily for skin conditions such as psoriasis.
- Aloe gel/mouthwash to be used twice or thrice daily (spat out afterwards).
- 100 ml of aloe gel twice daily for inflammatory problems (over a duration of 4 weeks and monitored by a physician).
- Used directly, small powders (100 grams) are boiled and drained twice or thrice a week.

Aloe vera Side effects, Interactions and Contraindications
Not recommended in:
- Old people with bowel obstruction.
- Pregnant and lactating women.
- Children younger than 12 years.
Aloe Vera side effects include:
- Diarrhea and vomiting.
- Skin allergies in some people.
- Interference with menstrual symptoms/cycle.
- Kidney toxicity in high doses
NB– Aloe vera is not recommended to be taken alongside antidiabetic and antiplatelet medication due to potential hypoglycemic effects.


Leave a Reply